Ever tried using a website or app that just didn’t make any sense? Something so clunky and confusing you felt like tossing your device across the room? Yep, that’s a prime example of poor UI/UX design. In this piece, we’re going to break down what UI and UX design really is, point out their similarities, and differences, and explain why they’re super important to get right. User interface (UI) and user experience (UX) are two vital components of app and web design that often get conflated. They are often misconstrued as the same thing, however, they are related but two distinct aspects of how users interact with a product. In this beginner’s guide, we will explore UI and UX design in more detail, their differences, and their importance in creating great products.
What is UI/UX Design?
UI/UX design refers to the process of designing digital products, such as websites, mobile apps, or software, to make them easy, intuitive, and enjoyable for users to interact with. Lets make it more clear with an example: Imagine throwing a party where everyone has a fantastic time. UI (User Interface) is like the party’s visual design – the decorations, layout, and organization that make it visually appealing. Just as arranging seating areas and choosing the right decor sets the mood at a party, UI design focuses on creating an attractive digital environment. Color schemes, fonts, and the arrangement of elements on the screen all work together to catch the user’s eye.
However, a visually stunning interface alone is not enough. Enter UX (User Experience). Think of this as the overall feeling and ease-of-use your friends have when they attend your party. UX design ensures that digital products are intuitive, functional, and free from confusion or frustration. Like planning a seamless party experience, UX design prioritizes user satisfaction through simple navigation, clear information organization, and responsiveness to user feedback.
Relationship between UI and UX Design
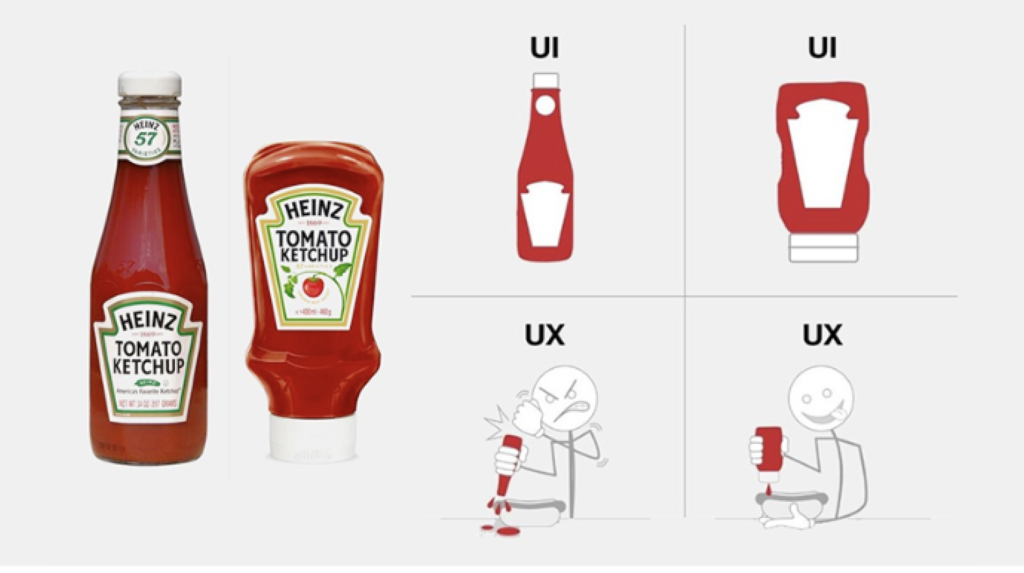
Let us be more clear about the relationship between them with an example. Imagine the evolution of ketchup bottles as a practical lesson in UI and UX design. The classic glass ketchup bottle, with its sleek design and unmistakable label, encapsulates the essence of User Interface (UI) design—it’s visually appealing but not particularly user-friendly. The ketchup rests at the bottle’s bottom, often stubbornly clinging to the glass far away from the lid. This inconvenient detail spotlights a key component of User Experience (UX) design—the ease with which users can interact with the product. In response to this challenge, Heinz innovated with a new plastic bottle, thoughtfully designed with the lid at the bottom. This pivotal change wasn’t just a facelift to the UI design, but a strategic enhancement of the UX. Now the ketchup naturally settles near the opening, ready to be dispensed without hassle, which is a clear demonstration of the company’s dedication to improving user experience, as illustrated in the image below.
Exploring more UI Design
UI design, or User Interface design, is a design discipline that focuses on creating visually appealing interfaces for digital products such as websites, mobile apps, and software applications. UI design focuses on the graphical elements of the interface, such as colors, typography, buttons, icons, and layout. Designers aim to create interfaces that are visually attractive, intuitive to navigate, and pleasant to use. By paying attention to aspects like visual hierarchy, use of white space, and consistent branding, UI designers ensure that the interface is visually cohesive and enhances usability.
Here are some key aspects of UI design:
Visual Elements: UI design incorporates various visual elements like buttons, icons, typography, color schemes, and layouts. These elements are carefully chosen and designed to convey information, guide user actions, and create a visually pleasing experience.
Consistency: Consistency plays a crucial role in UI design. UI designers strive to maintain visual consistency throughout the product, ensuring that similar actions or functions are presented consistently across different screens or pages. Consistency helps users understand and predict how the interface works, improving their overall experience.
Visual Hierarchy: UI designers use visual hierarchy to prioritize elements on the screen. By assigning visual weight to certain elements through size, color, and placement, designers can guide users’ attention to important information or actions. This helps users navigate the interface more easily and efficiently.
Feedback and Responsiveness: UI design includes incorporating feedback mechanisms and designing responsive elements. Feedback signals, such as hover effects or button animations, provide users with visual cues that their actions are registered by the system. Responsive elements adjust their appearance based on user interactions, enhancing the sense of direct manipulation and making the interface more intuitive.
Accessibility: UI designers also consider accessibility when creating the designs. They ensure that the interface is usable and understandable for people with disabilities by considering factors like color contrast, font size, and alternative text for images. Accessible UI design promotes inclusivity and ensures that everyone can use the product effectively.
Design Patterns: UI designers often leverage design patterns, which are established solutions for common design problems. These patterns provide users with familiar interactions and know-how, reducing the learning curve and making the interface more intuitive. Design patterns also contribute to consistency and usability across different products and platforms.
Effective UI design seamlessly combines various design elements, such as colors, layout, typography, and imagery, to create visually appealing interfaces. However, it goes beyond aesthetics by placing a strong emphasis on enhancing the user’s interaction and overall experience. By carefully considering how users will interact with the interface, effective UI design aims to create intuitive and user-friendly interactions.
Exploring more UX Design

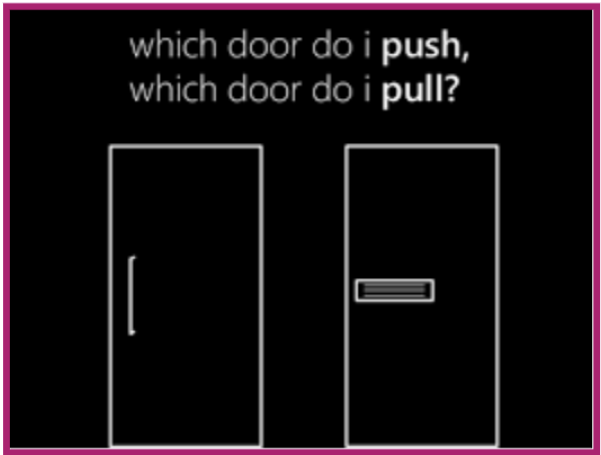
UX design encompasses the overall user experience of a product by focusing on the usability, accessibility, and emotional response of users. Lets take an example from Norman doors. Famously put by Don Norman, Norman doors, also known as “bad doors,” are those poorly designed entrances that often lead to confusion about whether to push or pull. Encountered in public spaces like offices and shops, these doors underscore the importance of intuitive design. By addressing their flaws, designers can create entrances that are both functional and user-friendly, enhancing the overall user experience.
Here are some key aspects of UX design:
User Research: UX designers conduct user research to understand user behaviors, needs, and pain points. This research involves techniques such as interviews, surveys, and observations to gain insights into user motivations, goals, and frustrations.
Persona Development: UX designers create personas, which are fictional representations of target users based on research findings. Personas help designers empathize with and design for specific user groups, ensuring that the product meets their needs and expectations.
Journey Mapping: UX designers create journey maps, which visualize the user’s interactions with the product over time. These maps help identify pain points and areas of improvement, allowing designers to optimize the user experience at each step of the user’s journey.
Prototyping: UX designers create prototypes to test and validate design solutions. Prototypes can be low-fidelity (sketches or wireframes) or high-fidelity (interactive designs). By testing prototypes with users, designers can gather feedback and refine the design to better meet user needs.
Usability Testing: UX designers conduct usability testing to evaluate the effectiveness and efficiency of the product’s design. Usability tests involve observing users as they interact with the product, identifying usability issues and areas for improvement.
Information Architecture: UX designers organize and structure the content and information within a product. This involves creating logical hierarchies, navigation systems, and labeling strategies that enable users to easily find the information they need.
While UI design primarily focuses on the visual aspects of an interface, UX design takes a holistic approach by considering the entire user journey. UX design is driven by extensive user research and analysis. This involves gathering insights about target users, their behaviors, and their pain points. Its goal is to provide a positive and satisfying experience for users. This entails removing obstacles and reducing frictions in the user journey, making interactions intuitive and easy to understand.
Importance of UI/UX Design
UI and UX may have distinct focuses, but they work together to create great products. Neither works well without the other – UX concepts need strong UI to come to life, while UI needs UX insights to guide it. When they operate in tandem, the user experience becomes greater than the sum of its parts. For anyone building apps or websites today, an understanding of UI/UX is essential. These disciplines provide the tools to make products that truly resonate with people. Paying attention to both visual design and experiential quality creates happy users, stronger engagement, and better conversions.
Keen on learning more about UI and UX design? You gotta read this book, seriously, it’s gold:
“The Design of Everyday Things”
It’s got everything you need to understand good design.

Snag it on Amazon: The Design of Everyday Things
And you know what? We love talking about UI/UX design here at Method Analytics. Check out what we do, shoot us a message, or just book some time to chat with us – we’re excited to help make your project awesome.
See what we do in UI/UX services
Let’s simplify the world through design together! 🚀






